Data Storage
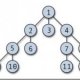
Database storage structures Database tables and indices are usually stored on a hard drive in one of the many forms, numbered / unnumbered Flat-Fails, ISAM, Pupils, Hash baskets or B+ trees. They have different advantages and disadvantages discussed in this section. B+ trees and ISAM are the most commonly used.
Arbitrary storage
Arbitrary storage - usually stored records in the order in which they were placed. While the efficiency of the bidding is good, it may appear that the extraction time would be ineffective, but this is usually never very important, as most databases use primary key indexes, resulting in or for the same keys as database lines shifted in the system file storage databases, resulting in more efficient searches.
Continuous storage
Consistent Storage - usually stored in order, and it may have to change or increase the size of the file if a new record is added, it's very inefficient. But it's better to look, because the records are pre-disposed than they can't brag.