Computer Data Storage
Introduction
The main purpose of the computer system is to carry out programmes. Programmes, together with data to which they have access, should, at least partially, be kept in operational memory. The operational system has to meet the challenge of sharing memory between the user processes and the components of the LO. This is called memory management. Thus, memory (storage, memory) is an essential resource that requires careful management. In the recent past, memory was the most expensive resource.
Part of the DS, which is responsible for memory management, is called memory manager.
Computer memory
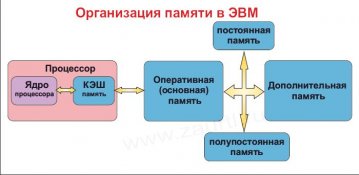
Memorial computer devices are divided at least by two levels: basic (primary, operational, physical) and secondary (external) memory.
Main memory is an orderly set of single-bite cells, each with its unique address (number). The processor extracts the team from the core memory, decodes and performs it. The team may need to be addressed to several other core memory cells. Basic memory is usually manufactured using semiconductor technologies and loses its contents when the power is disconnected.
Secondary memory (this is mainly disks) can also be considered as a single linear address space consisting of a bate sequence. Unlike operational memory, it is energy-dependent, has a substantially large capacity and is used as a major memory expansion.
This diagram can be complemented by several additional intermediate levels as shown in the figure. 8.1. Memory varieties can be merged into a hierarchy of losing access time, increasing prices and increasing capacity.
Rhys. 8.1. Memory hierarchy
The multi-level scheme is used as follows. The information that is stored at the top level is usually also stored at levels with large numbers. If the processor does not detect the necessary information at the i-level, it begins to look for it at the following levels. When the information needed is found, it's moving to faster levels.
Location
It turns out like that. mode of organization As the rate of access to memory is reduced, the frequency of its applications is also decreasing.
The nature of real programmes, for a limited period of time capable of working with a small set of memory addresses, plays a key role. This empirically observed characteristic is known as the principle of locality or localization of applications.