Storage Of Data In Oz
 2002 No. 4
2002 No. 4
When designing modern microprocessor systems, developers often face problems in choosing the appropriate type of replacement device. Frequently, there are contradictory requirements for the replacement device.
As a result, in many cases the memory area is divided into a number of separate blocks:
- Permanent memory. Relatively slow memory, intended primarily to store the work programme when eating off. In high-produced systems, a copy of the contents of the ELV in the fast-acting PES is being carried out in the process of operation.
- Rapid OPC. Designated for rapid storage of data during work. In a number of cases, in order to increase the system ' s speed in this area, OES is copied with the total or partial content of the ELV of programmes.
- Energy-dependent PES or electrically programmable ELV.
 Firstly designated for Long-term data storage (e.g. system configuration) when the power is off.
Firstly designated for Long-term data storage (e.g. system configuration) when the power is off.
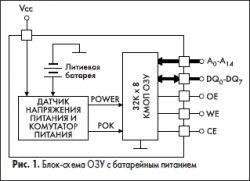
Over the years, there have been repeated attempts to bring together different memory areas of one device. One of the most successful solutions is the development of an energy-dependent POP with batteries.
Energy-dependent PHC with battery power
Such microwaves usually consist of a micro-schem of a super-male PPZ, a lithium power source and control circuits that connect a built-in source and lock the microschema when the power supply is lower than the allowed limit. A typical diagram of the device is shown in the figure. 1.